Run Lua script
Latest update: September 2017
Overview
This tutorial introduces the script execution function of FlashAir IoT Hub.
With the script execution function, you can execute arbitrary Lua script on FlashAir.
How script execution works
First of all, I will explain what kind of mechanism the script execution is realized.
Script execution is realized by polling on FlashAir and acquiring the job of FlashAir IoT Hub as follows.

-
Create job
When you enter the path and argument of the Lua script on FlashAir in FlashAir IoT Hub, its contents are registered as a job.
Multiple jobs can be registered, and wait for execution until it is acquired by FlashAir. -
Polling jobs
The Lua script on FlashAir checks the FlashAir IoT Hub for jobs at regular intervals. -
Execute job
If a job is found, it gets that job and runs on FlashAir.
Although it was possible to run Lua script via the Internet without using FlashAir IoT Hub, we needed the following preparations and knowledge.
-
Authentication
We set FlashAir's authentication method so that nobody can execute arbitrary Lua scripts. Access must be restricted. -
Access intermediary equipment and server
In order to connect to FlashAir from the Internet connection side, there are methods such as access via a network device such as a router or access via a server that FlashAir can communicate with.
However, the former requires advanced knowledge and experience of network and security, and the latter itself needs to prepare the server and its communication program.
FlashAir IoT Hub solves these problems by restricting access by safe and easy by using a token for communication with FlashAir and by setting FlashAir IoT Hub as an access mediation server.
Also, in script execution, you can use it with confidence without using FlashAir on the Internet by using the job mechanism.
How to operate the screen
Let's learn how to use script execution next.
Execute script
Specify the path and argument (optional) of the Lua script you want to execute and click the Execute button.
Please note that the Lua script to be executed must be placed on FlashAir in advance.

Path
Specify the file path of the Lua script on FlashAir.
Argument
Arbitrary arguments can be specified in the Lua script to be executed. Arguments must be specified in JSON format. You can specify only one argument, but you can specify multiple values by using JSON's array format or the like.
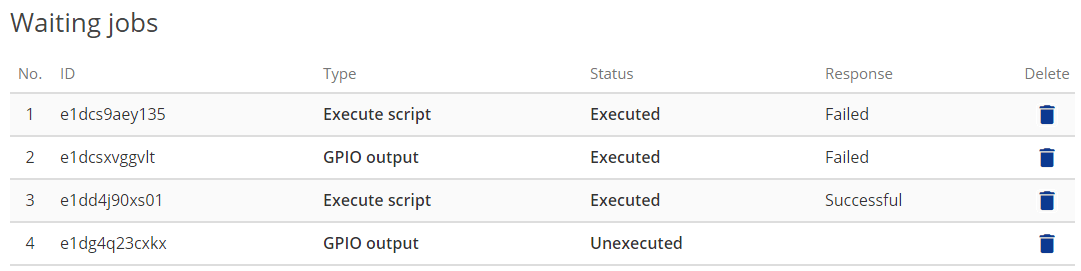
Waiting jobs
The path and argument of the entered Lua script are registered as a job and displayed in the list.
Here you can check the job execution status and execution result.
-
ID
An alphanumeric character string that uniquely represents the job. -
Type
It indicates the type of job. There are two types of GPIO output and Execute script. -
Status
Represents the job status. The state transitions to Unexecuted, Running, Executed. -
Response
Represent job execution results as Successful or Failed. -
Delete
Click the trash can icon to delete the job. If an unexecuted job is deleted, that job will not be executed.
Let's use script execution
Finally, let's actually use script execution.
Preparing for script execution
As an example we will create a Lua script that registers the value of the argument entered in FlashAir IoT Hub
as a
measured value.
Save the following Lua script in the root directory of FlashAir.
echo.lua
local iothub = require("iothub")
if type(arguments) == "table" then
iothub.addMeasurement(arguments)
sleep(30000)
iothub.addMeasurement(arguments)
end
-
Line 2:
Arguments specified in FlashAir IoT Hub are automatically set to the variableargumentsby converting JSON format values into Lua variables.
Ifargumentsis of the same table type as the argument ofiothub.addMesurement(), we will process it. -
Lines 3-5:
Send the value ofargumentsto FlashAir IoT Hub as measured value iniothub.addMesurement().
Set sleep so that the display of the graph is easy to understand, and send it twice.
Also edit the sample script
bootscript.lua that can be downloaded from FlashAir IoT Hub as follows and save it in the root
directory.
bootscript.lua
local iothub = require("iothub")
-- iothub.startPioUpload(0x03)
-- iothub.stopPioUpload()
local cnt = 0
while(1) do
iothub.runJob()
--iothub.addMeasurement({10, 20, cnt})
--cnt = cnt + 1
sleep(10000)
collectgarbage("collect")
end
-
Line 8:
Executeiothub.runJob()to execute the job if you can get the job from FlashAir IoT Hub. -
Lines 9, 10:
Comment out measurement value transmission processing so that the measurement value sent withecho.luais easy to understand.
You are now ready to run the script.
Running the script
Let's execute script from FlashAir IoT Hub.

Enter
/echo.lua for the path and
[40, 50] for the argument and click the execute button.


The script was executed and succeeded. Let's take a look at the measured value graph.

You should be able to see that the measured values sent in
echo.lua are reflected in the graph.
Preliminary preparation of Lua script enables detailed control such as acquisition and setting of GPIO and sensor data, so please make use of the script execution function of FlashAir IoT Hub by all means.
 FlashAir™ Developers
FlashAir™ Developers